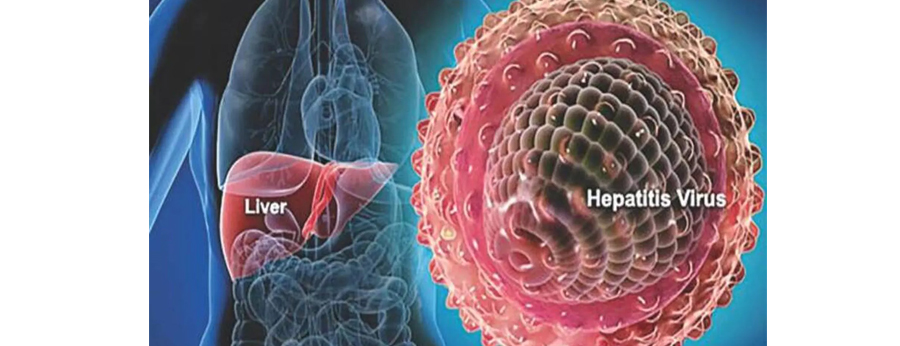
Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). For most people, hepatitis B is short term, also called acute, and lasts less than six months. But for others, the infection becomes chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. Having chronic hepatitis B increases your risk of developing liver failure, liver cancer or cirrhosis — a condition that permanently scars the liver.
Most adults with hepatitis B recover fully, even if their symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a long-lasting hepatitis B infection. This is known as a chronic infection.
A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but there's no cure if you have the condition. If you're infected, taking certain precautions can help prevent spreading the virus to others.
Symptoms of acute hepatitis B range from mild to severe. They usually appear about 1 to 4 months after you've been infected, although you could see them as early as two weeks after you're infected. Some people, usually young children, may not have any symptoms.
Hepatitis B signs and symptoms may include: